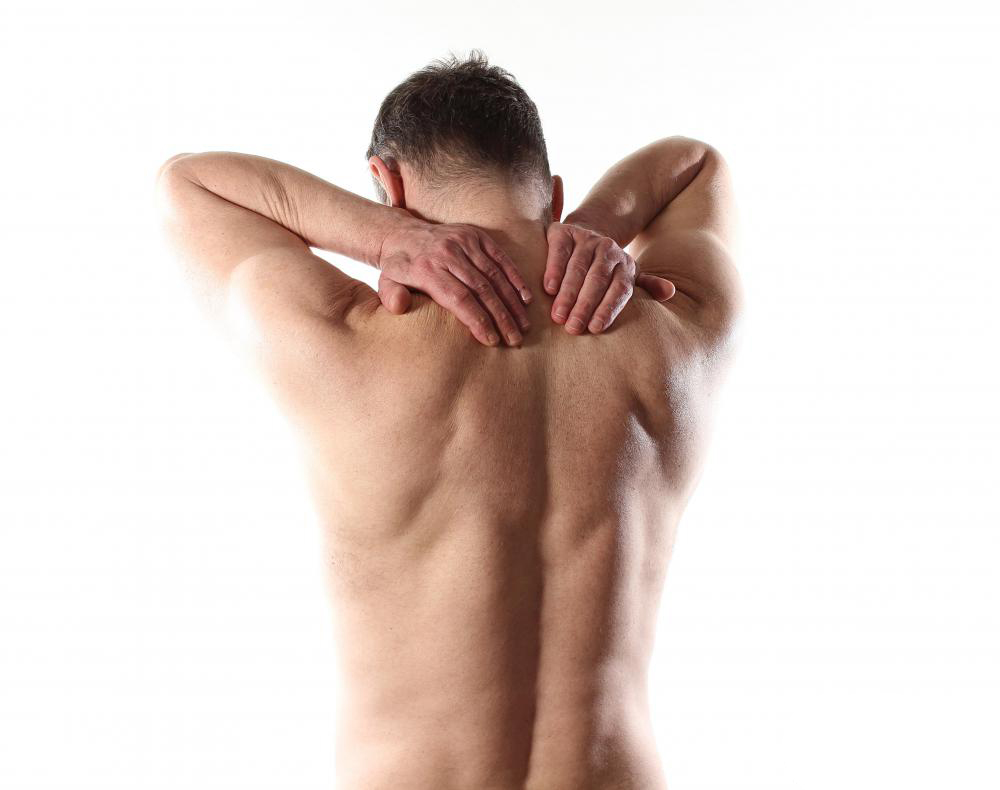
In the intricate web of human health, the link between our thoughts, emotions, and physical well-being is undeniable. Psychosomatic disorders, though often misunderstood, shed light on the profound connection between our mental and physical states. In this article, we’ll explore the concept of psychosomatic disorders, delve into their causes, symptoms, and offer insights into managing and preventing these complex conditions.
Understanding Psychosomatic Disorders
A psychosomatic disorder refers to a condition where psychological factors, such as stress, anxiety, or emotional distress, contribute to the onset, progression, or exacerbation of physical symptoms. Contrary to common misconceptions, psychosomatic disorders are not imaginary or “all in the head.” Instead, they highlight the intricate interplay between our mind and body.
Common Psychosomatic Disorders
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): IBS is characterized by gastrointestinal symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits. Stress and anxiety can exacerbate these symptoms.
- Migraine Headaches: Migraines often have triggers related to stress, anxiety, and emotional factors. Emotional stress can lead to the constriction and dilation of blood vessels, triggering migraines.
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS): CFS involves persistent fatigue that isn’t relieved by rest and is often accompanied by cognitive difficulties. Emotional distress can contribute to the severity of symptoms.
- Fibromyalgia: Fibromyalgia is marked by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and sleep disturbances. Stress and emotional factors can intensify pain perception.
Causes of Psychosomatic Disorders
- Stress and Emotional Factors: High levels of stress, anxiety, and unresolved emotional issues can contribute to the development of psychosomatic symptoms.
- Mind-Body Connection: The brain and body share intricate pathways that influence hormonal, immune, and nervous system responses.
- Past Trauma: Past traumatic experiences can lead to the manifestation of physical symptoms as a way of coping with emotional distress.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
- Physical Symptoms with No Clear Cause: Psychosomatic disorders often present with physical symptoms for which no organic cause can be identified.
- Symptoms Aggravated by Stress: Physical symptoms may worsen during times of increased stress or emotional turmoil.
- Normal Test Results: Diagnostic tests may show no abnormalities despite the presence of significant symptoms.
Managing Psychosomatic Disorders
- Mind-Body Techniques: Mindfulness meditation, deep breathing, and progressive muscle relaxation can help manage stress and alleviate physical symptoms.
- Counseling or Therapy: Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or psychodynamic therapy, can address underlying emotional issues and their impact on physical health.
- Healthy Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and adequate sleep contribute to overall well-being and may alleviate symptoms.
- Stress Management: Develop healthy coping strategies for managing stress, such as engaging in hobbies, spending time with loved ones, or pursuing relaxation techniques.
Preventing Psychosomatic Disorders
- Self-Care: Prioritize self-care and emotional well-being by engaging in activities that bring joy, practicing relaxation, and seeking support when needed.
- Emotional Awareness: Stay attuned to your emotions and address them in healthy ways rather than suppressing or avoiding them.
- Communication: Open and honest communication with loved ones can help prevent emotional distress from manifesting as physical symptoms.
- Mindfulness Practice: Regular mindfulness practice can help you manage stress and cultivate a healthy mind-body connection.
Psychosomatic disorders underscore the intricate relationship between our mental and physical well-being. By understanding the role of emotions, stress, and past experiences in contributing to physical symptoms, we can take proactive steps to manage and prevent these conditions. Remember that seeking professional guidance, practicing self-care, and cultivating emotional awareness are crucial aspects of maintaining a balanced and harmonious mind-body connection. As you strive to foster emotional well-being and address the root causes of distress, you empower yourself to lead a healthier and more fulfilling life.