Our thoughts have a profound impact on our emotions and behaviors, shaping our experiences and influencing our mental well-being. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely recognized approach that empowers individuals to reshape their thought patterns, leading to healthier emotions and behaviors. In this article, we’ll explore the principles of CBT, its benefits, and how it can help you take control of your mental health and lead a more fulfilling life.
Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
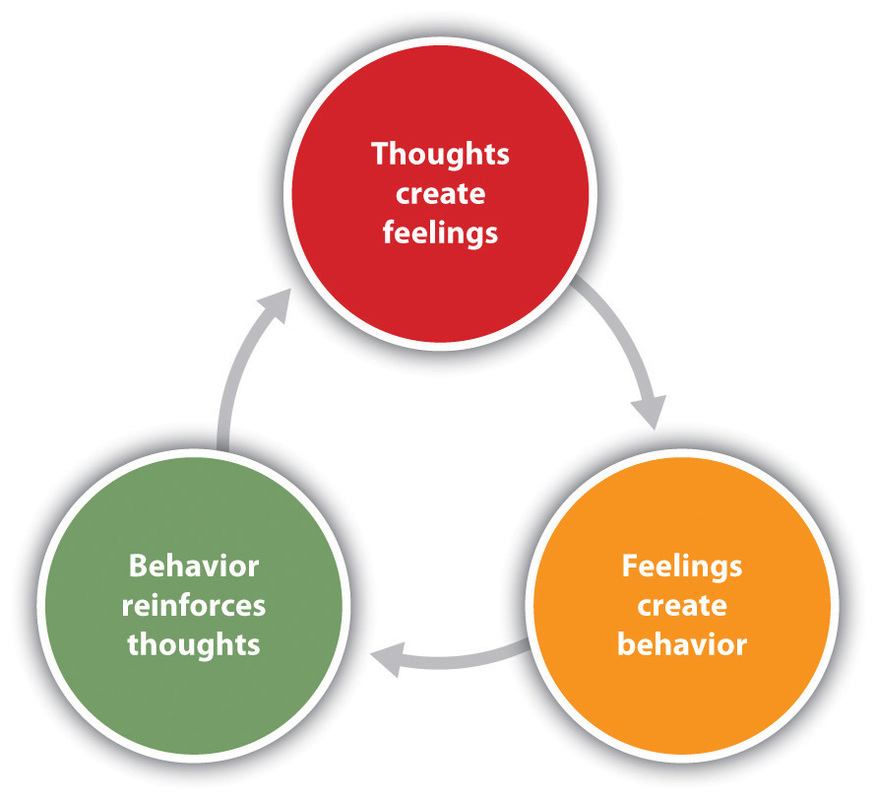
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a goal-oriented psychotherapy that focuses on the connection between our thoughts, feelings, and actions. Developed in the 1960s, CBT is based on the idea that negative thought patterns contribute to emotional distress and maladaptive behaviors. The therapy aims to identify and challenge these negative thought patterns, promoting positive change and improved mental well-being.
Key Principles of CBT
- Thought Awareness: CBT emphasizes becoming aware of your thoughts, recognizing the connection between thoughts and emotions.
- Cognitive Restructuring: This principle involves identifying and challenging irrational or negative thought patterns and replacing them with more realistic and balanced thoughts.
- Behavioral Activation: CBT encourages individuals to engage in activities that bring joy and a sense of accomplishment, counteracting negative emotions.
- Homework Assignments: Therapists often assign homework that involves practicing new skills and techniques outside of therapy sessions.
- Skill-Building: CBT equips individuals with practical skills to manage stress, anxiety, and depression through effective problem-solving and coping strategies.
Applying CBT in Daily Life
- Identify Negative Thoughts: Pay attention to your thoughts, especially those that contribute to negative emotions. Ask yourself if these thoughts are rational and evidence-based.
- Challenge Negative Thoughts: When you catch yourself thinking negatively, challenge those thoughts by asking for evidence and considering alternative perspectives.
- Replace with Positive Thoughts: Replace negative thoughts with more balanced and positive ones. Focus on realistic and constructive thinking.
- Practice Mindfulness: Mindfulness techniques can help you stay present, manage stress, and avoid getting caught up in negative thought cycles.
- Engage in Positive Activities: Participate in activities you enjoy to boost your mood and counteract negative emotions.
Benefits of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Effective for Various Conditions: CBT has been proven effective in treating a wide range of mental health conditions, including anxiety, depression, phobias, and more.
- Practical Strategies: CBT equips you with practical skills that can be applied in daily life to manage emotions and cope with challenges.
- Empowerment and Control: By learning to reshape your thought patterns, you regain a sense of control over your emotions and behaviors.
- Improved Relationships: CBT can enhance communication skills and reduce interpersonal conflicts by promoting more rational thinking and effective problem-solving.
- Lasting Results: CBT often leads to long-lasting results, as it provides individuals with tools to manage future challenges and prevent relapses.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) offers a transformative approach to managing emotions, improving mental well-being, and fostering personal growth. By understanding the connection between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, you can learn to challenge negative thought patterns and replace them with more balanced and constructive ones. Integrating CBT principles into your daily life empowers you to take control of your mental health, leading to improved relationships, enhanced emotional resilience, and a journey toward self-discovery and well-being. Whether you’re dealing with specific mental health challenges or simply seeking to cultivate a more positive and balanced mindset, CBT can provide you with valuable tools to navigate life’s ups and downs with greater ease and confidence.