In the journey of life, our emotions and thoughts play a significant role in shaping our experiences. Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (R.E.B.T.) is a powerful approach that helps individuals understand and reshape their thought patterns to achieve emotional well-being. In this article, we’ll explore the principles of R.E.B.T., its benefits, and how it can empower you to take control of your thoughts, emotions, and ultimately, your life.
Understanding R.E.B.T.
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy, developed by psychologist Albert Ellis in the 1950s, is a cognitive-behavioral approach that focuses on identifying and challenging irrational beliefs that lead to emotional distress. The goal of R.E.B.T. is to help individuals replace self-defeating thoughts with more rational, constructive beliefs, leading to healthier emotions and behaviors.
Key Concepts of R.E.B.T.
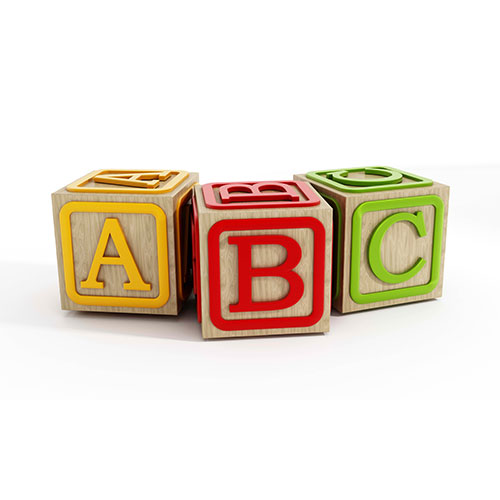
- ABC Model: R.E.B.T. uses the ABC model to explain the relationship between activating events, beliefs, and emotional consequences:
- A (Activating Event): An external event or situation triggers thoughts and beliefs.
- B (Belief): Irrational or rational beliefs arise in response to the activating event.
- C (Consequence): Emotional and behavioral consequences follow based on the individual’s beliefs.
- Irrational Beliefs: R.E.B.T. identifies common irrational beliefs, known as “Musts” and “Shoulds,” that contribute to emotional distress. Examples include the belief that things must go your way or that others should treat you a certain way.
- Rational Beliefs: Rational beliefs are flexible, adaptable, and based on reality. They are characterized by acceptance, preference, and constructive thinking.
- Disputing Irrational Beliefs: R.E.B.T. encourages individuals to challenge irrational beliefs through rational, evidence-based arguments. This process involves disputing the validity of irrational beliefs and replacing them with more rational alternatives.
Applying R.E.B.T. in Everyday Life
- Identify Irrational Beliefs: Become aware of irrational beliefs that contribute to emotional distress. Pay attention to thought patterns that start with “must,” “should,” or “ought.”
- Question Beliefs: Ask yourself if your beliefs are realistic, evidence-based, and helpful. Challenge irrational beliefs by examining their validity.
- Replace with Rational Beliefs: Replace irrational beliefs with rational alternatives. Focus on accepting reality, setting preferences, and practicing self-compassion.
- Practice Disputation: When faced with irrational thoughts, dispute them using rational arguments. Emphasize the lack of evidence supporting irrational beliefs.
- Develop Cognitive Flexibility: Cultivate the ability to adapt and reframe situations with a rational, constructive mindset. This reduces emotional distress and promotes resilience.
Benefits of R.E.B.T.
- Emotional Resilience: R.E.B.T. equips you with tools to handle emotional challenges by replacing irrational beliefs with rational ones.
- Reduced Anxiety and Depression: Challenging irrational beliefs can alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression, leading to improved mental well-being.
- Enhanced Self-Esteem: By embracing rational beliefs, you foster a positive self-image and self-worth, promoting healthy self-esteem.
- Improved Relationships: R.E.B.T. empowers you to communicate more effectively and manage conflicts by replacing rigid beliefs with adaptive thinking.
- Personal Growth: Embracing rational beliefs enhances personal growth, self-awareness, and the ability to navigate life’s ups and downs.
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy offers a transformative approach to managing emotions, thoughts, and behaviors. By identifying and challenging irrational beliefs, you can reshape your mindset, enhance emotional well-being, and cultivate healthier relationships. Integrating the principles of R.E.B.T. into your daily life empowers you to take control of your emotional experiences, leading to greater resilience, improved mental health, and a more fulfilling journey toward personal growth and self-discovery.