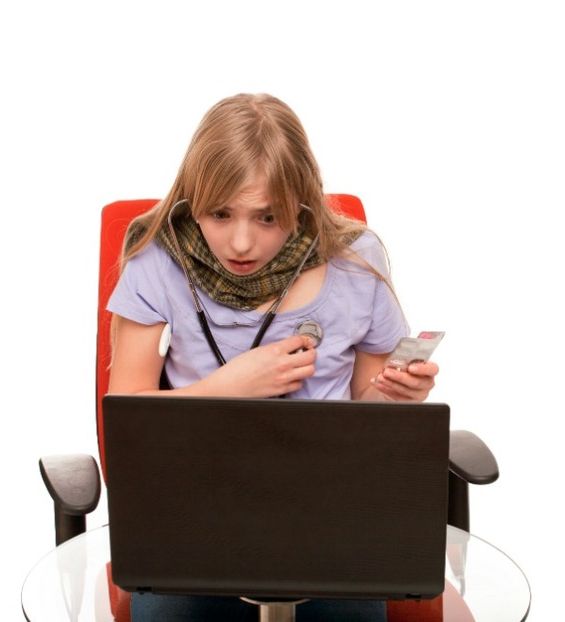
In a world where information is readily accessible, concerns about our health can sometimes spiral into a state of constant worry. Hypochondria, formally known as illness anxiety disorder or health anxiety, is a psychological condition that causes individuals to excessively fear having a serious medical condition. This article aims to shed light on the nature of hypochondria, its causes, common symptoms, and effective strategies for managing health-related anxiety.
Defining Hypochondria
Hypochondria, often referred to as health anxiety, is characterized by persistent and intense fears of having a serious illness, despite little or no medical evidence supporting the presence of the feared condition. Individuals with hypochondria may constantly monitor their bodies for potential symptoms, consult medical professionals frequently, and seek multiple medical opinions to alleviate their anxiety.
Key Characteristics of Hypochondria
- Exaggerated Concerns: Individuals with hypochondria tend to magnify and exaggerate minor bodily sensations, interpreting them as signs of a severe medical condition.
- Constant Checking: A hallmark of hypochondria is persistent checking of the body for symptoms, often leading to heightened anxiety.
- Medical Reassurance: Despite reassurances from medical professionals, individuals with hypochondria may continue to doubt their health status.
- Jumping to Conclusions: Individuals may quickly jump to the worst-case scenario when experiencing bodily sensations, assuming the presence of a serious illness.
- Time and Energy Consuming: The excessive worry and preoccupation with health consume a significant amount of the individual’s time and energy.
Causes of Hypochondria
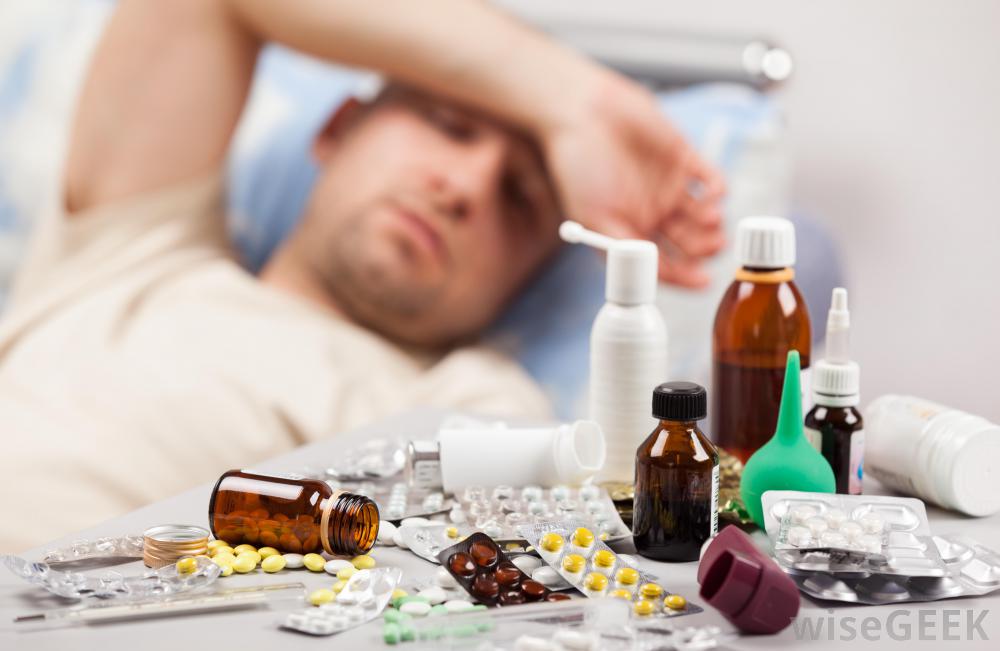

The origins of hypochondria can be multifaceted and may include:
- Genetics: A family history of anxiety disorders may increase the likelihood of developing hypochondria.
- Past Medical Experiences: Traumatic or distressing medical events in the past can contribute to health-related anxiety.
- Personality Traits: Individuals with certain personality traits, such as perfectionism or high levels of anxiety, may be more prone to hypochondria.
- Cognitive Factors: Distorted thought patterns, such as catastrophizing or magnification, can fuel health-related anxiety.
Managing Health Anxiety
Managing hypochondria requires a holistic approach that addresses both the psychological and physical aspects of the condition:
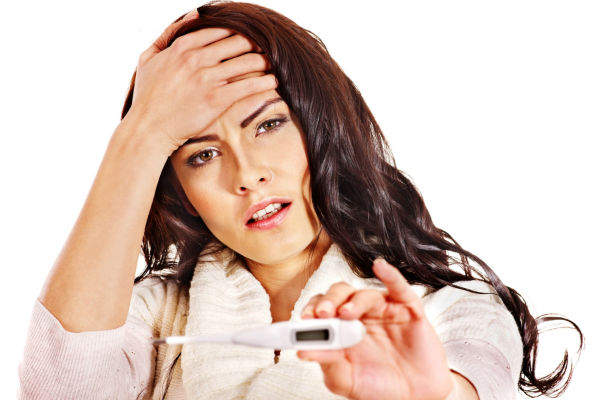

- Educate Yourself: Learning about the nature of health anxiety and understanding that it is a treatable condition can be empowering.
- Set Time Limits: Allocate a specific time each day to address health concerns. Outside of this designated time, try to redirect your focus to other activities.
- Practice Mindfulness: Mindfulness techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, and grounding exercises, can help reduce anxiety and bring you back to the present moment.
- Challenge Negative Thoughts: Question the validity of your health-related thoughts and consider alternative explanations for bodily sensations.
- Limit Medical Seeking: Reduce the frequency of seeking medical reassurance. Gradually decrease the number of medical appointments and consultations.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is an effective therapeutic approach for managing hypochondria. It helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with health anxiety.
- Professional Support: Seeking help from a mental health professional, such as a therapist or counselor, can provide guidance and tailored strategies for managing health-related anxiety.
The Path to Peace of Mind

Overcoming hypochondria is a journey that requires patience and commitment. Keep these points in mind as you work towards managing health anxiety:
- Progress, Not Perfection: Small steps towards reducing health-related anxiety can lead to significant improvements over time.
- Focus on Wellness: Redirect your energy towards adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep.
- Celebrate Achievements: Acknowledge and celebrate your achievements, whether it’s reducing the frequency of medical appointments or challenging negative thoughts.
- Support Network: Share your struggles with a trusted friend or family member who can provide encouragement and understanding.
- Be Kind to Yourself: Remember that managing hypochondria is a process, and setbacks are a normal part of growth.
Hypochondria, or health anxiety, can cast a shadow of worry and uncertainty over daily life. By understanding the characteristics, causes, and effective strategies for managing health-related anxiety, you can take steps towards regaining control over your thoughts and emotions. Seeking professional support and implementing self-care practices can pave the way to a life where peace of mind takes center stage, allowing you to focus on what truly matters – your overall well-being.