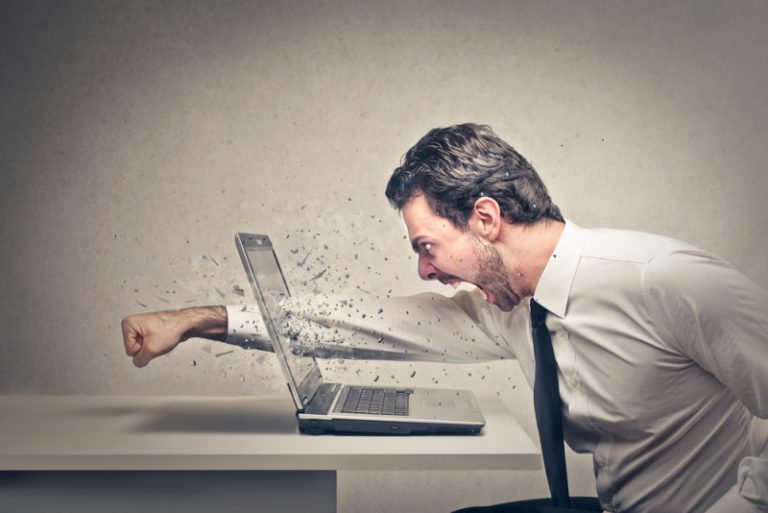
Emotions are an intrinsic part of the human experience, and anger is one of them. While anger itself is a natural response to various situations, obsessive anger management poses unique challenges that can impact our well-being and relationships. In this article, we’ll explore the concept of obsessive anger management, its causes, symptoms, and offer insights into healthy ways to manage and navigate intense emotions.
Understanding Obsessive Anger Management
Obsessive anger management refers to a pattern of intense and overwhelming anger that dominates a person’s thoughts, actions, and interactions. Unlike healthy anger expression, where emotions are acknowledged and addressed, obsessive anger management involves a heightened and prolonged focus on anger-related thoughts, often leading to maladaptive behaviors.
Common Signs of Obsessive Anger Management
- Repetitive Thoughts of Anger: Obsessive anger management is marked by relentless and intrusive thoughts about perceived injustices or triggers.
- Inability to Let Go: People struggling with this condition often find it challenging to move past their anger, holding onto resentment for extended periods.
- Disproportionate Reactions: Even minor triggers can evoke extreme and disproportionate anger reactions that may seem out of proportion to the situation.
- Difficulty in Problem Solving: Instead of effectively addressing the source of their anger, individuals with obsessive anger may focus on the anger itself, hindering problem-solving skills.
Causes of Obsessive Anger Management
- Unresolved Trauma or Stress: Past traumatic experiences or chronic stress can lead to heightened anger responses.
- Perceived Threats to Identity: Feeling threatened in terms of self-worth, status, or identity can trigger obsessive anger.
- Unhealthy Coping Mechanisms: Using anger as a way to cope with other emotions, such as sadness or anxiety, can reinforce its obsessive nature.
- Modeling Behavior: Witnessing obsessive anger expression in early life can influence how one manages anger later on.
Coping Strategies for Obsessive Anger Management
- Mindfulness and Self-Awareness: Practicing mindfulness helps you stay present, understand your triggers, and respond thoughtfully instead of impulsively.
- Pause and Reflect: When anger arises, take a moment to reflect before reacting. Consider the situation and whether your anger is proportionate.
- Healthy Outlets for Expression: Channel your anger into constructive outlets like journaling, exercise, or creative activities.
- Communication Skills: Learn effective communication techniques to express your emotions and needs without resorting to obsessive anger.
- Stress Reduction Techniques: Engage in stress-reducing activities like deep breathing, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation.
Seeking Professional Help
- Therapeutic Intervention: Counseling or therapy can provide you with tools to manage obsessive anger, understand its underlying causes, and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
- Anger Management Programs: Enrolling in anger management programs can offer structured guidance and support.
- Individual or Group Therapy: Both individual and group therapy can help you learn from others’ experiences and gain insights into managing anger.
Obsessive anger management can have a significant impact on our mental health, relationships, and overall well-being. By recognizing its signs, understanding its causes, and employing healthy coping strategies, you can navigate the challenges posed by this condition. Remember that seeking professional help is a crucial step in managing obsessive anger. With the right resources, support, and a commitment to personal growth, you can gain control over your anger, develop effective communication skills, and lead a more balanced and fulfilling life.