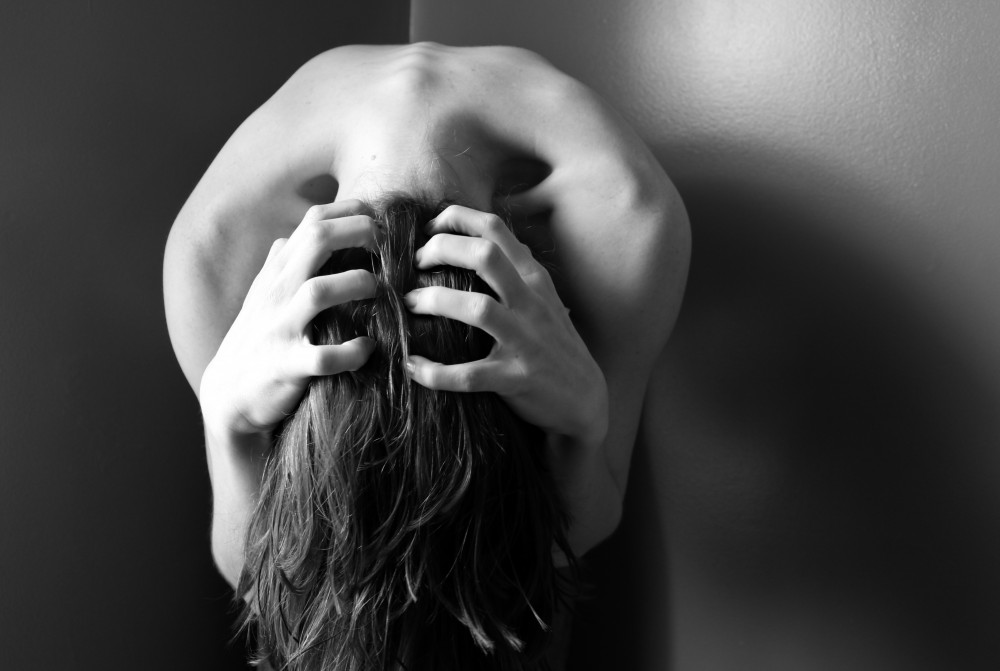
In the realm of emotions, anxiety is a familiar term that often conjures up feelings of unease or worry. But is anxiety just a passing feeling we all experience, or can it evolve into something more serious? In this article, we’ll explore the nature of anxiety, from its role as a natural human emotion to its potential manifestation as an anxiety disorder. By shedding light on this spectrum, we aim to provide a clearer understanding for a general audience.
The Basics of Anxiety: A Natural Emotion
Anxiety is a normal human emotion that surfaces when we encounter uncertain, stressful, or potentially dangerous situations. Often referred to as the “fight or flight” response, anxiety is a built-in survival mechanism that alerts our bodies to potential threats. This primal instinct can help us react swiftly when faced with danger, ensuring our safety.
Common Triggers of Anxiety
- New Experiences: Starting a new job, moving to a different place, or trying something unfamiliar can trigger anxiety due to the uncertainty involved.
- Social Situations: Meeting new people or speaking in public may lead to feelings of anxiety, especially if the fear of judgment is present.
- Academic or Professional Challenges: Exams, presentations, and performance evaluations can evoke anxiety due to the pressure to perform well.
Anxiety Disorders: A Complex Spectrum
While anxiety is a normal emotion, it can transform into an anxiety disorder when feelings of worry and fear become excessive, persistent, and disruptive to daily life. Anxiety disorders encompass a range of conditions, each with its unique characteristics and symptoms.
Types of Anxiety Disorders
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Characterized by excessive worry about various aspects of life, even when there’s no apparent reason.
- Panic Disorder: Involves sudden and intense panic attacks accompanied by physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat and shortness of breath.
- Social Anxiety Disorder: Marked by an intense fear of social situations and a strong desire to avoid them due to concerns about judgment or embarrassment.
- Specific Phobias: Involves an intense fear of a specific object, situation, or activity, which leads to avoidance behavior.
Distinguishing Factors: Natural Anxiety vs. Anxiety Disorders
- Duration and Intensity: Natural anxiety usually subsides as the triggering situation resolves. In contrast, anxiety disorders involve persistent, overwhelming feelings of worry that impact daily life.
- Functioning Impairment: Anxiety disorders can interfere with relationships, work, and overall quality of life, whereas natural anxiety is generally manageable and temporary.
- Excessive Avoidance: Anxiety disorders often lead to avoiding situations or places to prevent anxiety triggers, while natural anxiety may lead to brief avoidance.
Managing Anxiety: Effective Strategies for Both Ends
- Healthy Coping Mechanisms: Engage in activities that promote relaxation and stress reduction, such as deep breathing, mindfulness, and physical exercise.
- Balanced Lifestyle: Prioritize sleep, nutrition, and regular exercise, as they contribute to overall well-being and anxiety management.
- Seeking Support: For severe anxiety or anxiety disorders, seeking professional help from therapists, counselors, or psychiatrists is vital.
- Challenge Negative Thoughts: Learn techniques to identify and challenge irrational thoughts that contribute to anxiety, fostering a more balanced perspective.
Anxiety exists on a spectrum, ranging from a natural human emotion to anxiety disorders that require attention and support. It’s crucial to recognize the difference between normal anxiety and the point at which it becomes a disorder. By understanding the triggers, symptoms, and management strategies, individuals can navigate the spectrum with greater awareness and resilience. Remember that seeking professional help is a proactive step toward managing anxiety disorders effectively. With the right tools, support, and a balanced approach, individuals can lead fulfilling lives while addressing anxiety concerns.